Designing for laser cutting or other cutting processes is a lot different then traditional graphic design. It is not possible to just laser cut an image that is drawn on the computer. It is however, not difficult to design for laser cutting. Any graphic designer can make a design that is cnc laser, plasma, or waterjet cuttable if they learn the correct process, and use a vector based graphic design software.
Laser cutters are very accessible to anyone who wants to cut something out of metals, plastics, foam and natural materials like wood, leather, cloth. Graphic design typically deals with images or media that will be viewed on the web, TV or printed. These images are not suitable for laser cutting, and must be modified or retraced.
Use Vector Design Software
The first step is to use the correct software for designing an object to be laser cut. The design software must be vector based.
- Raster Image Software (Does not work for laser cut designs)
- Adobe Photoshop
- Gimpshop
- Corel Paint
- Vector Image Software (Good for laser cut designs)
- Adobe Illustrator
- Corel Draw
- Solidworks (2D export .dxf)
- Autocad (.dxf)
- ProE (2D export .dxf)
The following image shows the difference between a raster image, and a vector image.
- A raster image is composed of individual pixels, and has a finite resolution. When zoomed into a raster image, the pixels become visible.
- A vector image is composed of curves that are controlled by nodes. There is no loss of resolution or pixelating when zooming into the image.

Curves Are The Cut Lines
When cutting, the laser follows the curves in the file. The curves should have the smallest width value that can be assigned. This is called different things in different software, like hairline or thinline. Usually the value must be set to less than 0.5pt line thickness.
Do not use fills for any of your objects. The fill can hide curves that the laser will cut, but you did not intend to have cut.
Check for any extraneous curves in your design. Remember, all curves will be cut by the laser, so delete any curves that you don’t want to be cut lines.
Check Your File in Wireframe Mode
Always double check your file in wireframe mode. This will usually reveal any problems with the design. What you see in wireframe mode is what will get cut on the laser.
Check For Overlapping Curves/Objects
Sometimes there can be several copies of the same curve or object overlaying itself. This will cause the laser to attempt to cut the same path several times. Check to make sure that each path only consists of a single curve.
Example Design Cleanup
The following vector image was sent by a client. The first indication that this won’t cut well is that there are multiple color shades. That means that each shaded area will have a border, which the laser will want to cut out (without spending extra time editing the file of course). The desired result was to cut around the edge of the black areas.

When we look at the design in Wireframe view, we can really see the mess that is hidden behind the fills and thick curves. Each one of those curves, if not deleted, will generate a cut line for the laser to follow. There are also lots of curves overlapping.
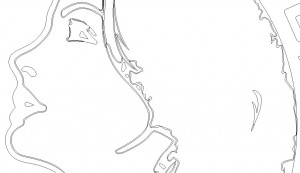
After some extensive cleanup, only the lines that we want to cut are remaining. This is now a clean design for laser cutting.

